Table of Contents
Sequence analysis of Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 markers
DESCRIPTION
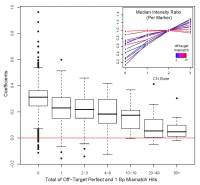
Duplicated regions, important for NAHR-mediated CNV formation, are represented on common oligi-nucleotode platforms. We observed that such regions require special attention due to possible cross-hybridization problems. To many locations in the human genome can be difficult to interpret, since a detectable variation in probe log2 intensity ratio may reflect copy number variation at one or several indistinguishable loci. Additionally, if a significant proportion of a probe's raw signal comes from cross-hybridization to (off-target sequences). As a quality control step prior to analyzing genomic data generated using the Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 platform, we flagged CN and SNP probes that align to multiple regions of the genome or that align to four or more locations with a single base pair mismatch (NCBI36/hg18). SNP genotype reproducibility was also tested.
DOWNLOADS
REFERENCES
Oldridge DA et al, Optimizing Copy Number Variation Analysis using Genome-Wide Short Sequence Oligonucleotide Arrays, Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jun;38(10):3275-86.